A Milestone for Crypto: What Do the Three Major Crypto Bills Mean for the Industry?
For years, the crypto industry has undergone wild, unchecked growth. But this week, the U.S. Congress is holding a pivotal “Crypto Legislation Week.” The GENIUS Act, CLARITY Act, and Anti-CBDC Act are coming together to form the most comprehensive regulatory framework in U.S. crypto history. These bills not only set clear compliance pathways but also block government-issued digital currency. If enacted, these three landmark laws could fundamentally reshape the $2.8 trillion cryptocurrency market.
The House votes on these critical crypto bills were just as dramatic. In the first round, several Republicans unexpectedly defected, prompting former President Trump to summon the twelve pivotal “core members,” whose votes could decide the outcome, into his office for talks. After nearly ten hours of negotiations, lawmakers ultimately overcame the deadlock with a procedural vote (deciding whether the bill could advance to a final vote)—marking the longest vote in Congressional history. This outcome set the stage for substantive debate on the Guiding and Enabling National Innovation in U.S. Stablecoins Act (GENIUS Act), the Digital Asset Market Clarity Act (CLARITY Act), and the Anti-CBDC Surveillance State Act.

Republican Dissenters Stand Up to Trump in a Record-Breaking Vote
At the center of the debate is the GENIUS Act, which would establish a federal regulatory framework for stablecoins. The CLARITY Act would clarify when crypto assets are classified as commodities or securities, drawing clear lines between oversight by the Commodity Futures Trading Commission (CFTC) and the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC). Meanwhile, the Anti-CBDC Act aims to ban any U.S. central bank digital currency (CBDC) to protect Americans’ financial privacy. If these bills become law, the industry would move from speculative, gray-area innovation to a new era governed by clear, actionable rules.
Congressional Journey: A Rocky Start
The GENIUS Act passed the Senate on June 17, 2025, with strong bipartisan support (68-30), setting the pace for U.S. crypto legislation. But House Republicans, led by Freedom Caucus Chair Andy Harris (R-MD), insisted on stronger anti-CBDC provisions before allowing the bill to move forward. On July 15, 2025, twelve House Republicans broke with Trump’s explicit orders and voted 196-223 to reject the rule required to bring the GENIUS Act to the floor. This rare GOP split hinged on the lack of a clear CBDC ban.
The twelve Republican defectors included prominent figures such as Marjorie Taylor Greene (R-GA), who opposed the bill “because it does not ban a central bank digital currency,” and Anna Paulina Luna (R-FL), who warned that it could inadvertently open the door to a CBDC. Their concerns reflected deep-seated ideological opposition to the government’s surveillance capacity inherent in a CBDC.
Without a CBDC ban, the Fed could create a digital surveillance state unprecedented in U.S. history, tracking every transaction in real time and eliminating the privacy provided by cash. The economic risks are just as severe—CBDCs could trigger massive bank runs as people shift deposits into Federal Reserve accounts, threatening the $18 trillion banking system’s stability.
Globally, 137 countries representing 98% of global GDP are exploring CBDCs, and China’s digital yuan is already in widespread use. Republican critics warn that without a clear ban, the U.S. could unwittingly embrace a “monetary surveillance tool” that fundamentally changes the relationship between citizens and their government.
Trump’s Oval Office Intervention
On the evening of July 15, Trump stepped in to break the deadlock. After meeting with eleven of the twelve dissenters in the Oval Office, Trump secured their commitment to a second vote through a carefully crafted compromise. The deal attached the Anti-CBDC Surveillance State Act to the National Defense Authorization Act and added “clear, strong anti-CBDC language” to the CLARITY legislation.
Trump posted on Truth Social: “After a brief discussion, they all agreed to vote for the rule tomorrow morning.” The personal intervention demonstrated Trump’s continued influence over the Republican caucus—even when challenged by its most conservative members.
The July 16 vote turned into the longest procedural vote in House history, stretching over ten hours as Republican leaders worked tirelessly to bridge factional divides. Late on Wednesday, Speaker Mike Johnson (R-LA) helped broker a final agreement, gradually dissolving opposition among the conservative bloc, and the measure passed by a narrow margin of 215-211.
With the rule approved, the stage is set for final votes on the GENIUS, CLARITY, and Anti-CBDC Acts. The GENIUS Act is expected to be the first major crypto law signed by a U.S. president, having already secured broad bipartisan support in both chambers and establishing federal-level rules for stablecoins.
The bill lays out tough new standards: stablecoin issuers must maintain fully backed 1:1 reserves in dollars or short-term Treasuries and disclose reserve composition monthly. This is designed to build legitimacy and confidence among banks, merchants, and everyday users. The CLARITY Act aims to clearly define when a crypto token is a commodity or a security, expanding the CFTC’s oversight of digital assets and reducing pressure on SEC enforcement. These moves show the U.S. is enacting real rules for the crypto market—long outside the boundaries of traditional finance.
The adopted rule established debate parameters for all three bills, paving the way for comprehensive regulation while maintaining GOP unity on broader legislative objectives.
Regulation Isn’t the End—It’s Crypto’s Second Act
For years, crypto operated as a kind of “legal experiment.” Bitcoin began as a rebellious digital money experiment, Ethereum brought a new technological paradigm, and innovations like DeFi, NFTs, GameFi, and tokenization of real-world assets emerged—all thriving in legal gray zones. But after FTX’s spectacular collapse in 2022, the industry’s story changed, with both markets and regulators pushing for clear rules.
This round of U.S. legislation is the answer to three big questions: Which stablecoins are legal? Which crypto assets are commodities, and which are securities? Who is responsible for overseeing this new financial ecosystem? Soon, federal law will provide clear answers. Once these details are in place, the industry can move from trial and error to a rule-bound growth path.
As Bitfinex Derivatives Head Jag Kooner observed, once a legislative framework emerges, institutional investors will return. These three bills create multiple regulatory pathways that will fundamentally reshape the crypto market—creating clear winners and losers among different sectors and projects.
How the GENIUS Act Will Transform Stablecoins
The now $190 billion-plus stablecoin industry faces the most immediate change. Circle’s USDC is likely to be a big winner, with 80% of its reserves in U.S. Treasuries and established bank partnerships, it already meets most regulatory requirements. Circle’s NYSE listing and partnership with BlackRock position the company perfectly for mainstream adoption within the new framework.
Tether, however, faces significant challenges to survive. With over 60% market share and $155 billion in circulation, Tether’s long-standing lack of audits and regulatory compliance will make meeting the GENIUS Act’s strict requirements difficult. The company must choose between expensive U.S. compliance (estimated at $2–5 million a year) or potentially leaving the U.S. market to focus on El Salvador and other unregulated regions.
Decentralized stablecoins like DAI will need major restructuring. Since 80% of DAI is backed by centralized stablecoins (mainly USDC), MakerDAO faces dependency issues and may need to boost its U.S. Treasury reserves from 10% to over 50% to comply with the new rules. The protocol’s DAO governance may also need changes to meet requirements for centralized decision-making.
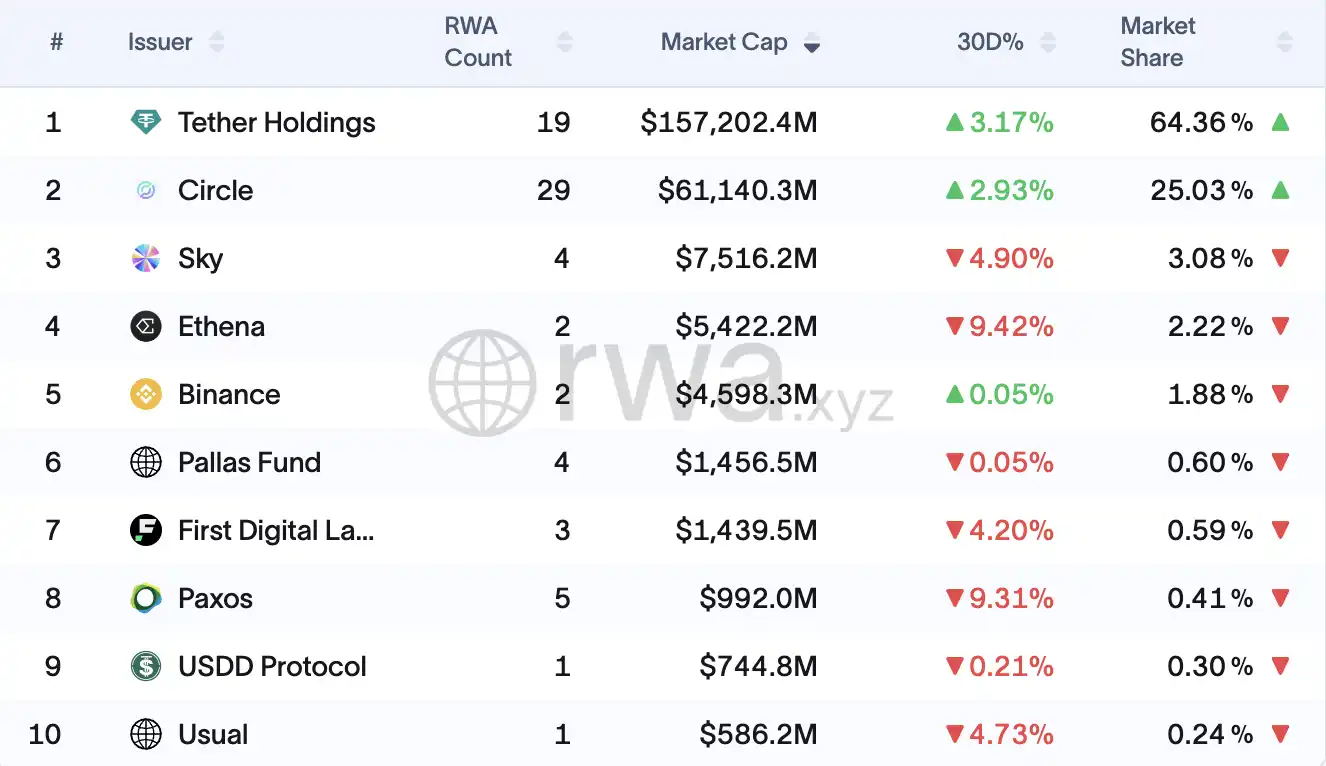
New market entrants must navigate $1–3 million in initial costs and $2–10 million in annual compliance expenses—major obstacles for startups, but new opportunities for traditional finance. Major banks, Visa, Mastercard, and fintech firms are gearing up to issue stablecoins, and the market could grow to $2 trillion by 2030.
The CLARITY Act: Certainty Brings Compliance Costs
The CLARITY Act gives digital assets their first clear regulatory framework by defining SEC and CFTC boundaries—but at the cost of new compliance burdens.
DeFi protocols face the toughest uncertainty. Uniswap and other decentralized exchanges will need to adopt centralized-style listing reviews and may need to register their user interfaces as broker-dealers. Lending protocols like Compound are moving to foundation structures for clarity, while showing enough decentralization to qualify for lighter regulation.
Small DeFi startups could face prohibitive compliance costs—$500,000 to $1 million a year—giving large, established players an advantage. Industry leaders warn this might drive “DeFi developers overseas” as teams are forced to centralize operations to satisfy regulators. Token projects must be reclassified as they shift from SEC-supervised “investment contract assets” to CFTC-supervised “digital commodities.” This will cause short-term price swings but offers long-term compliance certainty. Licensed, audited, SEC-registered or CFTC-registered exchanges will attract capital and users, while projects relying on ambiguity, cross-border operations, or regulatory arbitrage will be pushed out.
NFT platforms like OpenSea will gain clarity via possible exemptions from securities exchange rules, but must separate client and company funds. The law draws new lines between “digital commodities,” “investment contract assets,” and “non-commodity collectibles,” each with its own rules.
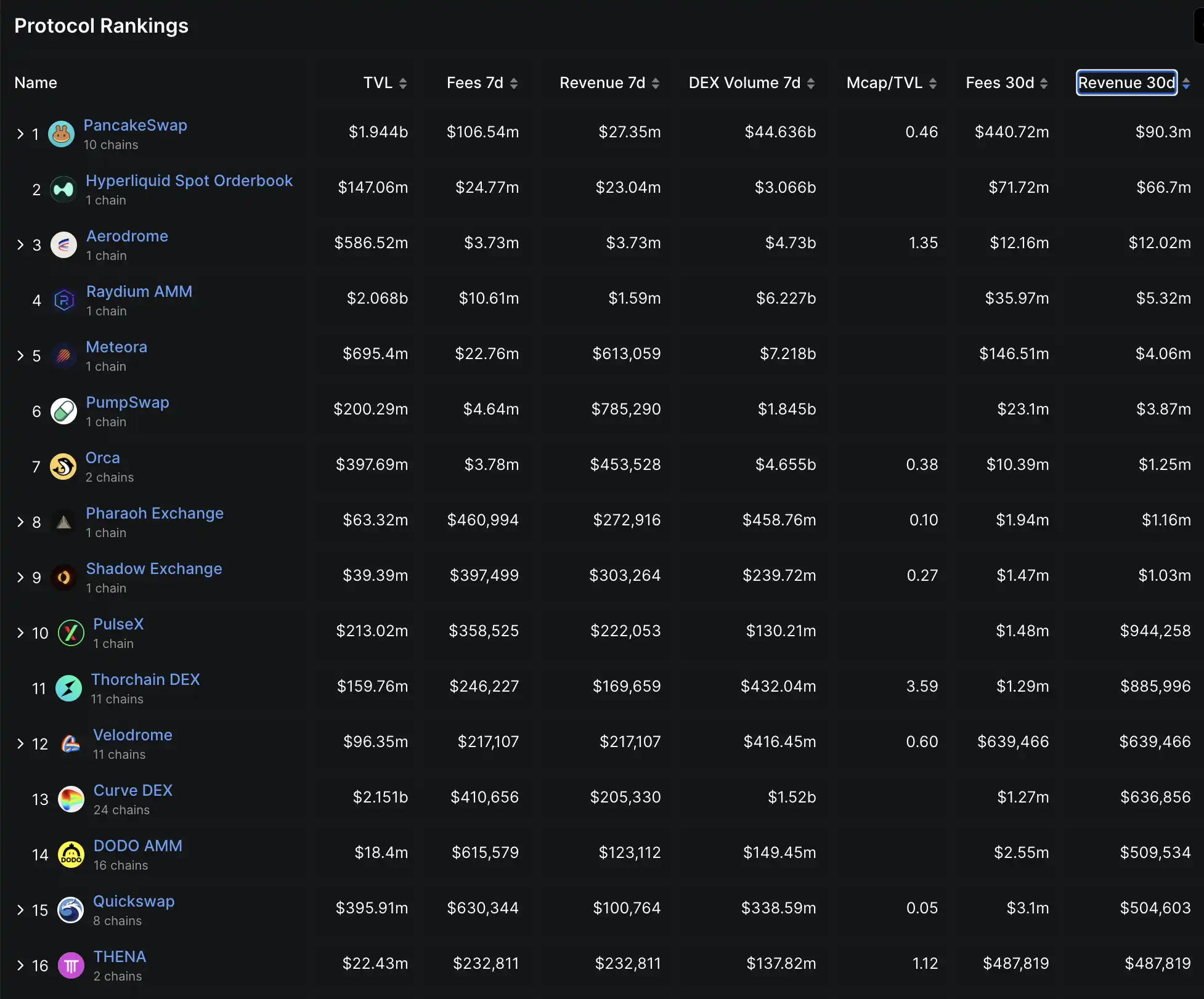
Fewer than 30 DeFi protocols generate more than $100,000 in monthly revenue. Source: Defillama
Centralized exchanges stand to benefit most from regulatory clarity, even though they face $10–50 million a year in dual SEC/CFTC compliance costs. Coinbase and other regulated platforms will gain a big edge over unregulated rivals and finally win access to institutional markets that regulatory uncertainty previously kept out of reach.
The Anti-CBDC Act: Guaranteeing the Private Sector’s Leadership
The Anti-CBDC Act delivers the private digital payments system’s most significant long-term protection. By banning the Fed from issuing a retail CBDC, the law eliminates government competition in digital payments, benefiting the entire private crypto ecosystem.
Stablecoin issuers will gain permanent protection from government competition, ensuring private stablecoins remain the dominant digital payment method. The ban will drive private innovation and shield legacy players like Visa and Mastercard from CBDC-based threats. Community banks are key winners—able to keep their deposits and lending bases free from government competition. The law stops the Fed from competing against retail banks and preserves banks’ role in U.S. credit creation.
This new era brings both opportunity and higher compliance costs: banks must spend $5–20 million to launch and regulate stablecoin operations, while payment processors will need to invest $2–10 million to enhance their AML/KYC systems. The new regulatory framework allows pension funds and asset managers to finally access the crypto market. U.S.-regulated crypto exchanges will grab market share while offshore platforms face rising costs. This gives U.S.-compliant platforms a clear edge in winning institutional capital.
The era of “arbitrary enforcement” by the SEC appears to be ending, with the CFTC positioned to become a leading digital asset regulator. Domestically built blockchain projects, regulated custody, and legally recognized stablecoins are all poised for revaluation. In short, the once unregulated, borderless crypto industry is entering a new era—clear rules, compliant operations, and much higher barriers to entry.
How Are Crypto Insiders and Wall Street Reacting?
The industry is broadly optimistic about this legislative wave. Steven Goldfeder, CEO of Offchain Labs (developer of Arbitrum), pointed out that regulatory risk has been the sector’s biggest uncertainty. “A legislative framework finally signals to the market that this technology is here to stay. It needs real governance—and trust can only be built within such a system.” Bitfinex’s Jag Kooner concurs, saying that even if the bills are not enacted, “the mere sign of legislative engagement is enough to boost market confidence.”
Meanwhile, traditional financial giants are moving in. Bank of America CEO Brian Moynihan revealed that the bank is considering a stablecoin, though there’s no firm launch timeline. He believes that as regulation becomes clear, stablecoin services will roll out as naturally as Zelle and Venmo did in mainstream banking. JPMorgan CEO Jamie Dimon has acknowledged “stablecoins are real” and said the bank will participate in building related infrastructure. This shows that both crypto-native teams and Wall Street giants are seizing this “watershed moment” to prepare for crypto’s move into mainstream finance.
Since Bitcoin’s beginning, the crypto industry has been locked in a tug-of-war with regulators. Now, Congress looks poised to deliver the first comprehensive answer—one that neither stifles nor ignores the industry. This isn’t the end, but a fresh start: a turning point where crypto’s self-governance gives way to institutional logic, and what was once a digital wild west is becoming a critical part of global financial infrastructure.
Legal Notice:
- This article was republished from [BLOCKBEATS], with copyright belonging to the original authors [BUBBLE, Lin Wanwan]. For republication questions, please contact the Gate Learn Team, and we will respond promptly according to our process.
- Disclaimer: The views and opinions in this article are those of the author and do not constitute investment advice.
- Other language versions were translated by the Gate Learn Team. Unless Gate is referenced, do not copy, distribute, or plagiarize translated articles.
Share
Content





